Before you can rank on Google, you need to understand how search engines work. This chapter breaks down how search engines work — so you can optimize smarter and rank faster.
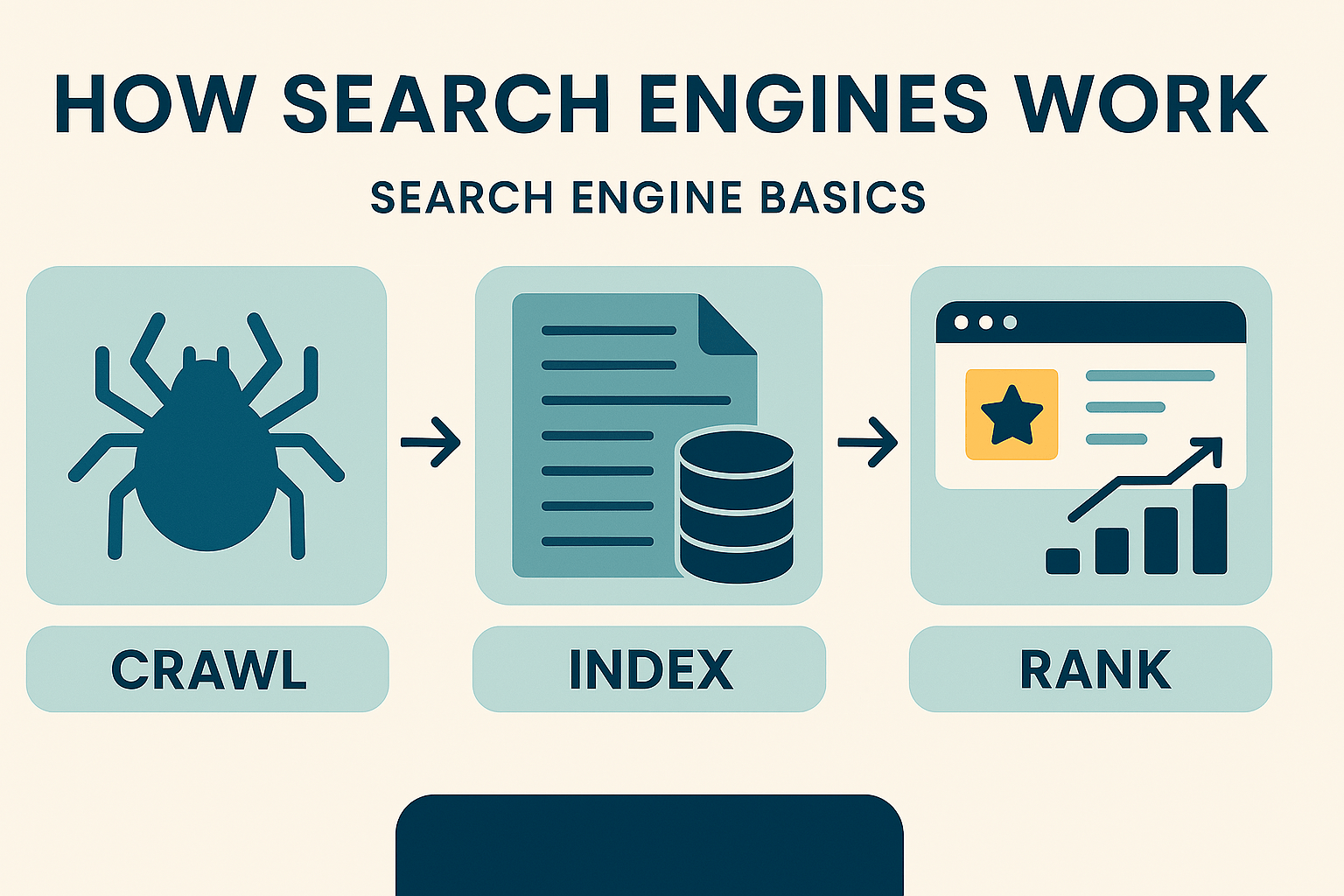
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a digital system that helps users find information on the Internet. The most popular one, Google, uses bots to scan, organize, and rank websites based on relevance and quality.
- Crawling – finding content across the web
- Indexing – storing & organizing content
- Ranking – showing the most relevant results
← Missed Chapter 1? Learn SEO Basics First
Step 1: Crawling – How Search Engines Discover Your Site
Google uses bots (called “spiders”) to scan the internet 24/7. When they land on your site, they follow links and read content. If your site is hard to crawl (e.g., broken links, no sitemap), it may never get indexed.
Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console to submit your sitemap and monitor crawl issues.
Step 2: Indexing – How Google Stores Your Content
After crawling, Google stores your pages in a massive database—called the index. But it only stores content that meets its quality, mobile, and security standards.
- Fast loading = more likely to index
- Mobile-friendly = better visibility
- Duplicate content = bad for indexing
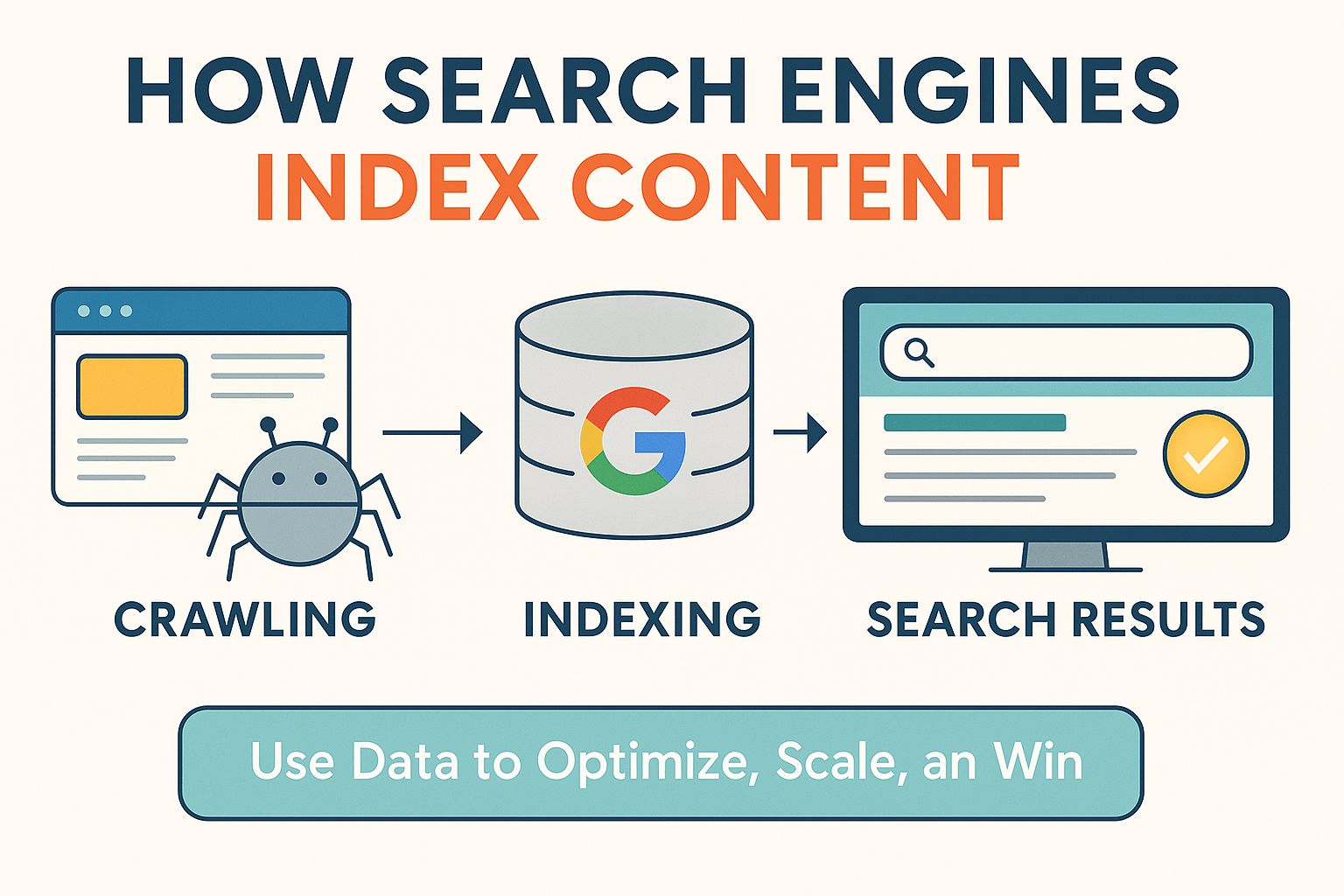
Tool: Use Screaming Frog to simulate how bots crawl & index your site.
Step 3: Ranking – How Google Decides What to Show
Google ranks pages based on over 200 factors—but a few matter more:
- Relevance to the search query (keywords)
- Authority (backlinks from trusted sites)
- User experience (bounce rate, time on site)
- Freshness & mobile speed
Quick Win: Optimize your titles, headings, and meta descriptions to improve CTR and rankings.
Conclusion: Know the System, Then Hack It
Understanding how search engines work gives you a massive advantage. When you optimize for crawlability, indexability, and relevance, you stop guessing and start ranking.
Next Read : Keyword Research for SEO →
Previous : SEO Basics – What Every Beginner Must Know →